J
John Iwuozor
Guest
Learn the best practices for authenticating users and granting access within you secure managed file transfer solution.
Transferring files requires strong security practices to help prevent data breaches and theft. As more people work remotely and information is shared across devices and networks, the risks are real. The good news, is with the right authentication and access controls, you can streamline your file transfer process while better protecting your data.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the best practices for verifying users, setting appropriate access levels and monitoring file transfer activities, so you can share files more confidently.
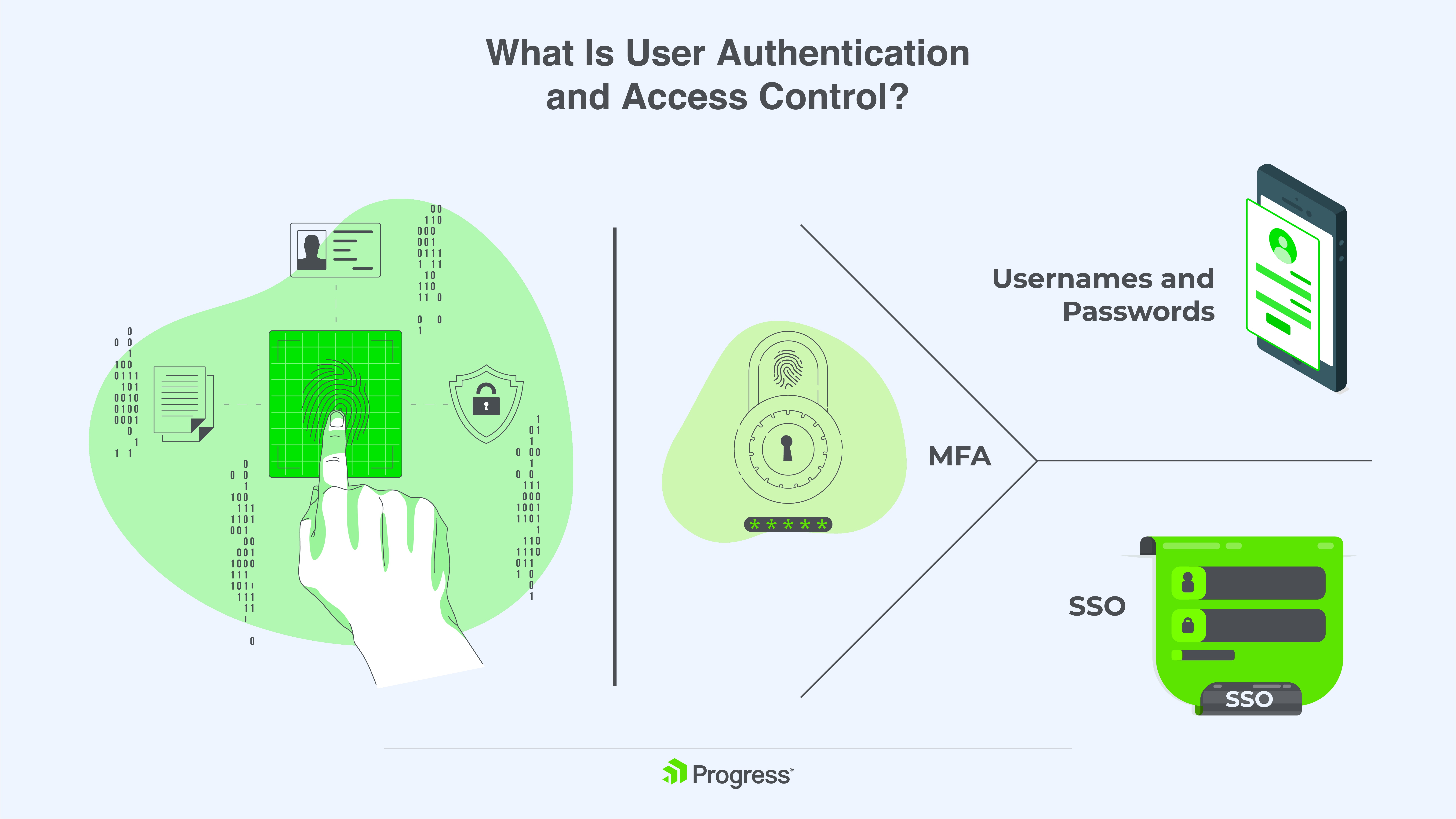
User authentication verifies who is accessing your files. The most common methods are username/password, multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO):
Once users are authenticated, access control determines which files and folders they can access. By setting up role-based access control (RBAC), you assign users only the permissions they need to do their jobs. This adheres to the principle of least privilege, reducing the risk of accidental or intentional data exposure.
Require users to create passwords with a minimum of eight characters, including a mix of letters, numbers and symbols. Longer, more complex passwords are harder to crack.
Place a limit on the number of failed login attempts to lock out bad actors. Around three to five failed attempts are typical before the account gets locked for a period of time. This deters brute force attacks, which try repeatedly to guess passwords or credentials.
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security for user logins. It requires not only a password but also a code sent to the user’s phone or an authentication app. This helps prevent unauthorized access if a password is stolen.
Assign specific access rights to users based on their role. Common roles include:
Once you define the roles, create them in your file transfer software. Then assign users to the appropriate roles based on their job functions and access needs.
As job roles change, permissions may need to be revised. Conduct reviews at least once a quarter to check that users still have appropriate access. Remove permissions immediately when a user leaves the organization.
Monitor user logins and file access to detect suspicious behavior early. Look for login attempts from unknown devices or locations, access to sensitive data the user does not normally need or downloads of large volumes of files. Investigate any anomalies right away.
Encrypt all data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access. Use strong encryption standards like Advanced Encryption Standard 256 ( AES 256) for data at rest and Transport Layer Security (TLS) for data in transit. Encryption should be applied automatically with no user intervention required.
When choosing a secure managed file transfer solution, it’s important to consider how it handles user authentication and access control. After all, you want to provide access to the right people and the right files, while also preventing any unauthorized access.
A good solution will support multi-factor authentication, like passwords plus one-time codes sent via text or app. This helps prevent account takeovers. It should also allow you to set password policies so that users must choose strong, unique passwords.
The solution should provide a way to create user roles with specific access permissions. For example, you may have roles like “Administrator,” “Power User” and “Standard User” with different levels of access. Users are assigned to the appropriate role. This makes it simpler to control who can access, upload, download, delete or modify files.
Look for a solution that logs user activities like logins, file uploads/downloads, permission changes, etc. These audit trails allow you to monitor how the system is being used and detect any unauthorized access. They provide visibility into who accessed what and when.
Ideally, the solution can integrate with your existing authentication systems like Active Directory or Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). This allows you to manage users and permissions in one place and have that information sync with your secure managed file transfer solution.
For maximum control, the solution should allow you to set permissions at the folder, subfolder and individual file levels. You can specify who has access to upload, download, modify, delete and more for each file or folder. This fine-grained control keeps users limited to the materials they have access to.
When it comes to secure managed file transfer solutions, proper user authentication and access control are crucial. Progress MOVEit is a simplified managed file transfer solution that provides advanced security features that help strengthen your security posture, right from the first transfer. It offers more granular user access controls, allowing permissions to be set based on a user’s business role and needs.
Additional security capabilities are provided through two-factor authentication and IP address restrictions, and it can be integrated with Active Directory and LDAP for user onboarding. MOVEit also logs various user activities and numerous file transfers, facilitating compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR and PCI DSS.
In essence, MOVEit delivers an enterprise-level solution for improved secure managed file transfers with wide-reaching control and visibility over user access and activity.
Start a free MOVEit trial
Continue reading...
Transferring files requires strong security practices to help prevent data breaches and theft. As more people work remotely and information is shared across devices and networks, the risks are real. The good news, is with the right authentication and access controls, you can streamline your file transfer process while better protecting your data.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the best practices for verifying users, setting appropriate access levels and monitoring file transfer activities, so you can share files more confidently.
What Is User Authentication and Access Control?

User authentication verifies who is accessing your files. The most common methods are username/password, multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO):
- For username/password, it requires complex passwords with a minimum of eight characters, including a mix of letters, numbers and symbols.
- MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring not just a password but also a code sent to your phone or an authentication app. This helps prevent unauthorized access even if your password is compromised.
- SSO allows users to sign in once with a single ID and password to access multiple services. This simplifies the login process for your users while still providing a secure authentication method.
Once users are authenticated, access control determines which files and folders they can access. By setting up role-based access control (RBAC), you assign users only the permissions they need to do their jobs. This adheres to the principle of least privilege, reducing the risk of accidental or intentional data exposure.
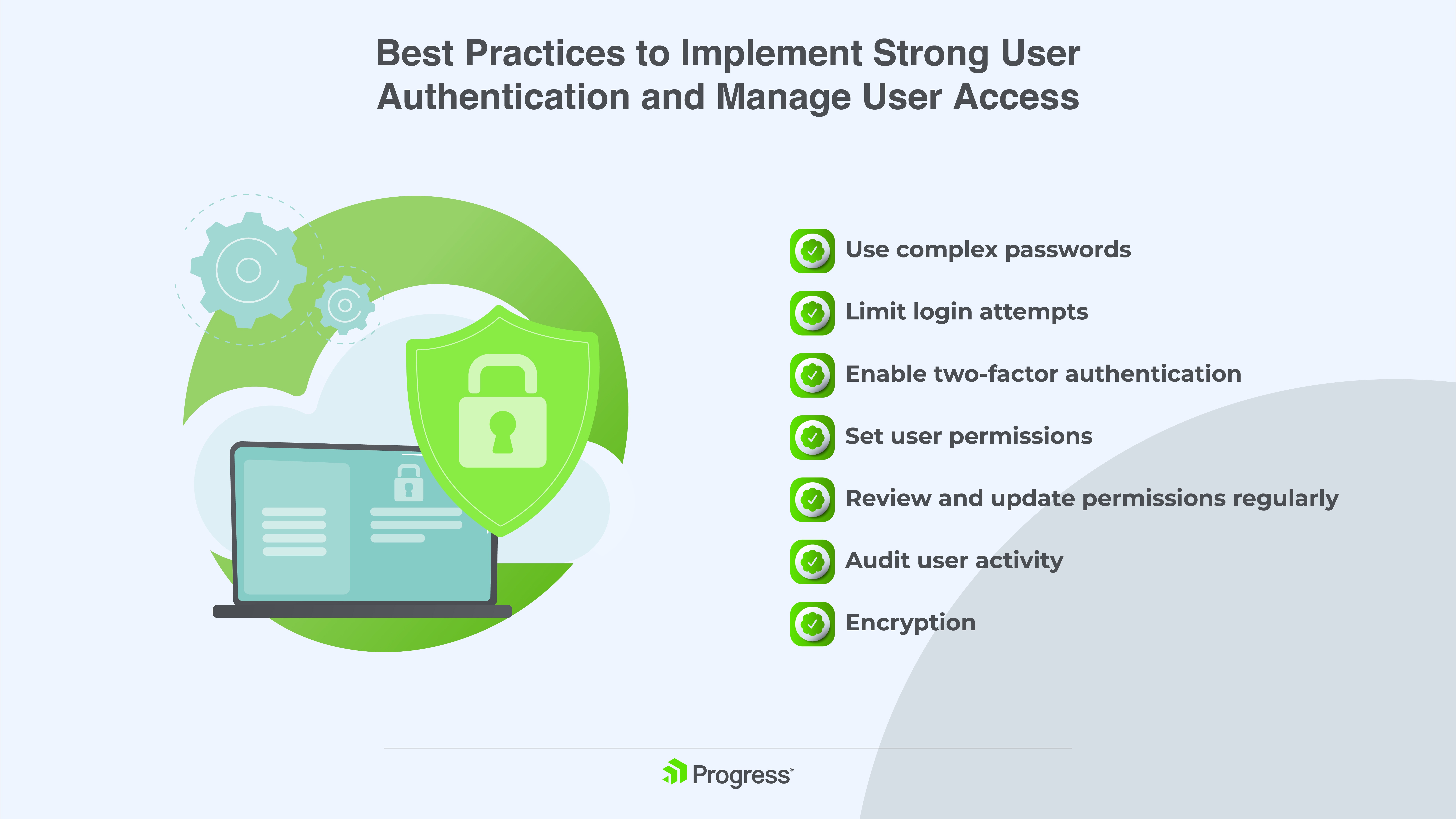
Best Practices to Implement Strong User Authentication and Manage User Access

Use Complex Passwords
Require users to create passwords with a minimum of eight characters, including a mix of letters, numbers and symbols. Longer, more complex passwords are harder to crack.
Limit Login Attempts
Place a limit on the number of failed login attempts to lock out bad actors. Around three to five failed attempts are typical before the account gets locked for a period of time. This deters brute force attacks, which try repeatedly to guess passwords or credentials.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security for user logins. It requires not only a password but also a code sent to the user’s phone or an authentication app. This helps prevent unauthorized access if a password is stolen.
Set User Permissions
Assign specific access rights to users based on their role. Common roles include:
- Admin: Full access to add, edit and delete users, files and folders.
- Power User: Can add, edit and delete most files and folders. Limited user admin rights.
- User: Basic access to upload, download, view and edit files.
- Read-Only: Can only view and download files. No edit or upload rights.
Once you define the roles, create them in your file transfer software. Then assign users to the appropriate roles based on their job functions and access needs.
Review and Update Permissions Regularly
As job roles change, permissions may need to be revised. Conduct reviews at least once a quarter to check that users still have appropriate access. Remove permissions immediately when a user leaves the organization.
Audit User Activity
Monitor user logins and file access to detect suspicious behavior early. Look for login attempts from unknown devices or locations, access to sensitive data the user does not normally need or downloads of large volumes of files. Investigate any anomalies right away.
Encryption
Encrypt all data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access. Use strong encryption standards like Advanced Encryption Standard 256 ( AES 256) for data at rest and Transport Layer Security (TLS) for data in transit. Encryption should be applied automatically with no user intervention required.
Choosing the Right Secure Managed File Transfer Solution
When choosing a secure managed file transfer solution, it’s important to consider how it handles user authentication and access control. After all, you want to provide access to the right people and the right files, while also preventing any unauthorized access.
Strong User Authentication
A good solution will support multi-factor authentication, like passwords plus one-time codes sent via text or app. This helps prevent account takeovers. It should also allow you to set password policies so that users must choose strong, unique passwords.
Role-Based Access Control
The solution should provide a way to create user roles with specific access permissions. For example, you may have roles like “Administrator,” “Power User” and “Standard User” with different levels of access. Users are assigned to the appropriate role. This makes it simpler to control who can access, upload, download, delete or modify files.
Audit Trails
Look for a solution that logs user activities like logins, file uploads/downloads, permission changes, etc. These audit trails allow you to monitor how the system is being used and detect any unauthorized access. They provide visibility into who accessed what and when.
Integration with Your Authentication Systems
Ideally, the solution can integrate with your existing authentication systems like Active Directory or Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). This allows you to manage users and permissions in one place and have that information sync with your secure managed file transfer solution.
Granular Folder and File Permissions
For maximum control, the solution should allow you to set permissions at the folder, subfolder and individual file levels. You can specify who has access to upload, download, modify, delete and more for each file or folder. This fine-grained control keeps users limited to the materials they have access to.
Concluding Thoughts
When it comes to secure managed file transfer solutions, proper user authentication and access control are crucial. Progress MOVEit is a simplified managed file transfer solution that provides advanced security features that help strengthen your security posture, right from the first transfer. It offers more granular user access controls, allowing permissions to be set based on a user’s business role and needs.
Additional security capabilities are provided through two-factor authentication and IP address restrictions, and it can be integrated with Active Directory and LDAP for user onboarding. MOVEit also logs various user activities and numerous file transfers, facilitating compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR and PCI DSS.
In essence, MOVEit delivers an enterprise-level solution for improved secure managed file transfers with wide-reaching control and visibility over user access and activity.
Start a free MOVEit trial
Continue reading...
